Optical Switching Fabrics for Scalable IP Routers
Project Description
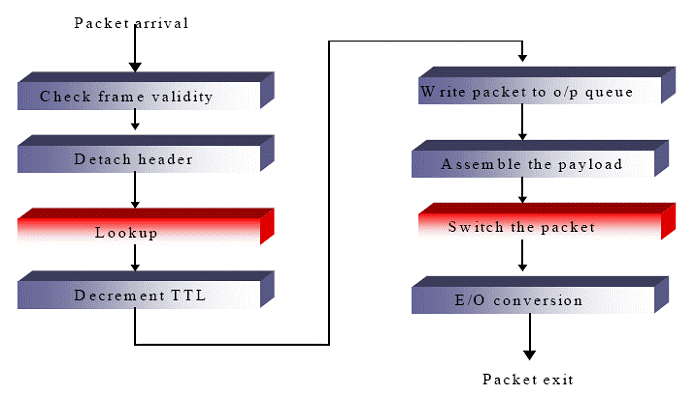
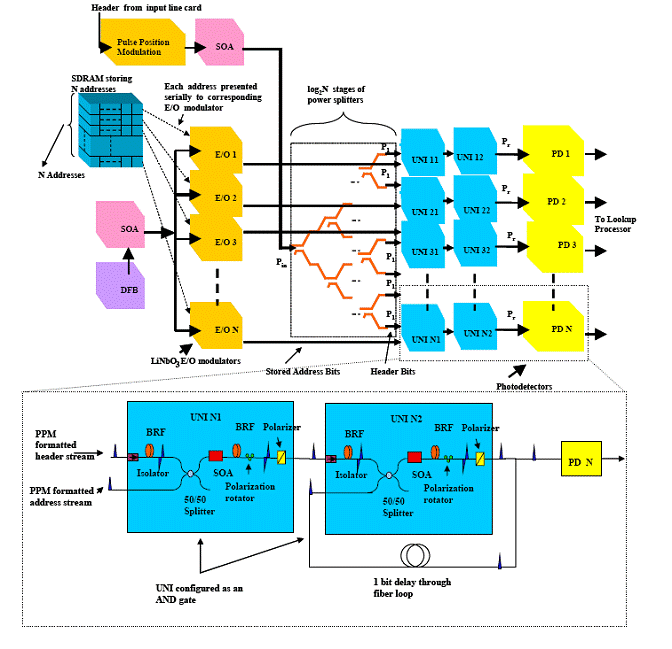
The increasing dependence of today's information infrastructure on the Internet is due partly to the robust and flexible IP and advancements in optical fiber communication technology. It has already been observed that the Internet traffic doubles every 1.8 years. IPv6 is already on its way with 128 bits allocated for each source and destination node. Broadband access technologies such as DSL, gigabit Ethernet access, voice and video communication over the Internet further the requirements for highly flexible, robust and high bandwidth Networking at low cost. Various bottlenecks in networking at high-speed and quality of service (QoS) have been recognized. The bandwidth limitation in copper for such high bandwidth transmission has forced the industry and research to deploy fiber optic links. With Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM), add-drop multiplexers, Optical cross-connects (OXC), high power lasers, it has been possible to transmit 100's of channels of digital information through optical fibers over long distances at low costs. Although this provides a high bandwidth in communication, a tremendous demand to catch up with the line speed is now placed on the intermediate nodes in the Internet or the “routers”. In order to meet the growing demand for performance at the routers, this project identifies the various functions executed on a single packet as it moves along the router and isolates some of the most time consuming subtasks. The most time consuming steps within the processing domain would be the ones that require communication with external memory and switching of a packet to its destination port. In other words, destination IP address “lookup” and “switching” would be the most time consuming steps in header processing. As the first phase in our research, this project tackles the “address recognition” issue or “lookup”.
Publications
R. Bhagavatula and A. Louri, “An Optically Assisted High Speed Scalable IP Router,” in IEEE Optical Communications, 2004.
P. Choo and A. Louri, “Guided-wave multiwavelength Content-Addressable Memory (CAM) processing module for database and networking applications,” in Proceedings of Optics in Computing 2001, Lake Tahoe, NV, 2001, pp. 1-7.